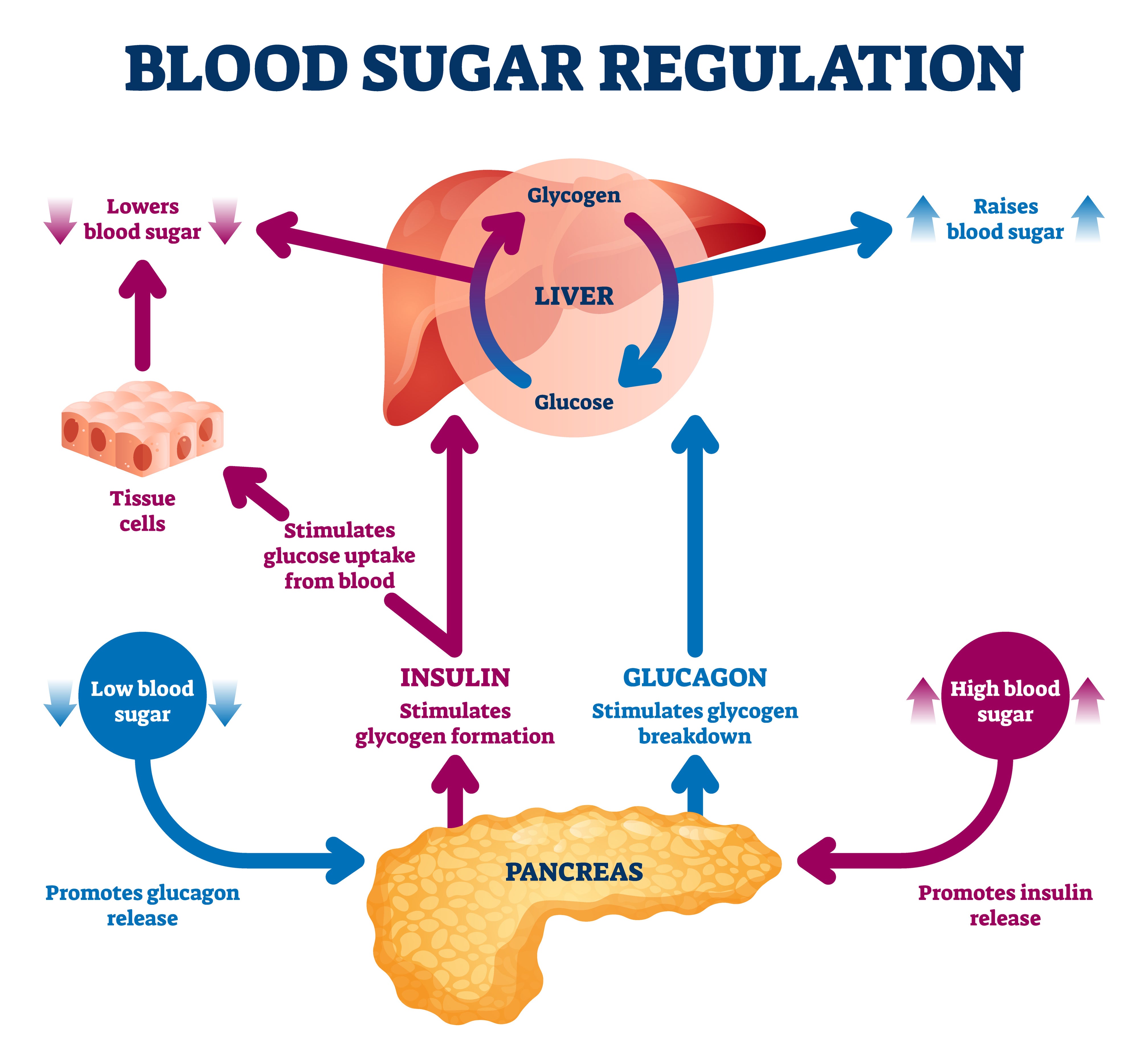


Supporting Systems and Interactions
The human body is a marvel of interconnected systems, each playing a vital role in maintaining balance, health, and vitality. While we often think of the body's organs and processes in isolation, the truth is that no part functions alone. Every system relies on and influences others in a delicate dance of cooperation.
When one system is compromised, others often compensate or respond, illustrating how deeply intertwined all functions are. The body, then, is not just a collection of parts, but an integrated whole, where every aspect plays a crucial role in maintaining the flow of life, energy, and healing. Understanding this interconnectedness allows us to approach health holistically, nurturing not just individual parts, but the whole person.
Supporting Systems
Hormones
What is necessary for the optimal health of this system?
Achieving and maintaining a balanced, healthy life requires a holistic approach that recognizes the complex interplay between nutrition, lifestyle, the use of herbs and supplements. Each of these elements plays a unique yet interconnected role in supporting the body's intricate systems.
Together, nutrition, lifestyle, and herbal support create a synergistic approach to health. They nurture the body as a whole, and support the body’s natural ability to heal, adapt, and flourish. Understanding the role each of these elements plays allows us to make more informed choices that contribute to lasting well-being.
Supporting Recipe

Black Bean Brownies
Ingredients
Supplies
Directions
Continue learning & exploring
Sugary Sweet Terminology
The Detrimental Effects of Sugar
Low Sugar Snacks
Healthier Holiday Sweets
The Benefits of Bitters
The Benefits of Walking
Explore These Supporting Products

Disclaimer: This content is for educational purposes only and is intended to support the understanding of an already healthy body. It is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. If you have or suspect a medical condition, or are considering changes to your health routine, please consult a licensed healthcare professional. This information has not been reviewed or approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Hello & Welcome
We believe people find us when they are meant to. Welcome to RidgeCrest Herbals, a small family-owned herbal supplement company based in Utah, and doing this work since 1994!. If you are new here, our content is written by real people on our team and inspired by our almanacs, customer swag, and the everyday conversations that fuel our love of herbs and helping others. We are a fun bunch who care deeply about sharing what health and wellness means to us in real life. We hope you stick around, explore our award-winning products and wellness almanacs, and get to know our company and team a little better.